This manual gives you a walk-through on how to train the logP Plugin:
Introduction
If you think your experimental data could improve the performance of the default logP calculator, you can take advantage of the supervised logP learning method that is built into the logP calculator.
If you create a local logP model, the scope of the logP calculator will be limited. It means that the calculated logP will only provide reasonable prediction for a few types of structures. Practically only those types of structures will be predicted correctly which were introduced to the training set during the teaching process. For example, if the training set contains only certain types of hydrocarbon but no other functional groups are present in the training set, the predicted logP of any amine-like molecule will not be accurate.
Therefore you need to be aware that a more robust general logP model requires a large, diverse training set with thousands of structures. You can generate a logP training library via cxcalc calculator functions or Instant JChem as well.
Training steps
Preparing the input file
As the first step of the training you have to create a training set from your experimental data. The training set should have a format which supports saving molecular properties (SDF or MRV). This can be easily done by using the graphical user interface of Instant JChem. This training set must contain the following items:
- structure
- logP values in a property field named LOGP
See this bit of an example file (logP_trainingset.sdf ).

Fig. 1 Example file used for training
Creating the training library
Then you have to run the training algorithm which creates a logP training library from your pre-compiled set. Execute the following command from command line:
cxtrain logp -t LOGP -i [library name] -a [training file]
Example
cxtrain logp -t LOGP -i mylogp -a logP_trainingset.sdf
The created logP training library mylogp can be used via MarvinSketch, cxcalc, or Chemical Terms.
Applying the training library
MarvinSketch
- Choose MarvinSketch menu Tools > Partitioning > logP.
- Select the User defined or the Weighted method to activate the training option.
- If you have created multiple training sets, choose the needed one from the dropdown list below the checkbox.
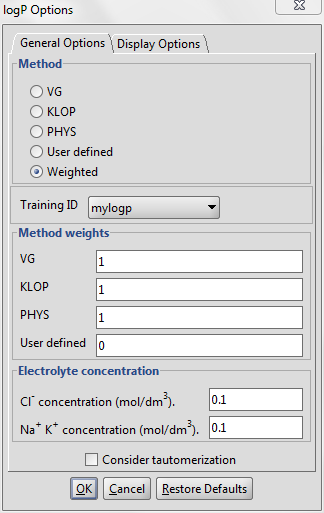
Fig. 2 logP options window showing how to apply the training library
Cxcalc
To apply your logP dataset use the --trainingid and the --method parameter:
cxcalc logp--method user --trainingid[library name] [input file/string]
Example
cxcalc logp --method user --trainingid mylogp "CC(C)CCO"
Result
id logP
1 1,13
Without training the result is:
id logP
1 1,09
Chemical Terms
Chemical Terms are available from Chemical Terms Evaluator or from Instant JChem. The method and trainingid parameters can be used in Chemical Terms Evaluator as well:
evaluate -e "logp('method:user trainingid:[library name]')" "[input file/string]"
Example
evaluate -e "logp('method:user trainingid:mylogp')" "CC(C)CCO"
Instant JChem
You can also apply your logP training library via Chemical Terms in Instant JChem.
- Choose the 'New Chemical Terms Field icon' on the panel on the right side.
- Type the chemical term into the window, use the parameters method and trainingid. Do not forget to adjust the Name, the Type and the DB Column Name.
Example
The following figure presents the usage of logP training in the 'New Chemical terms' window. The expression
logP('method:user trainingid:mylogp')
defines that the plugin use the user defined logP training library myplogp.
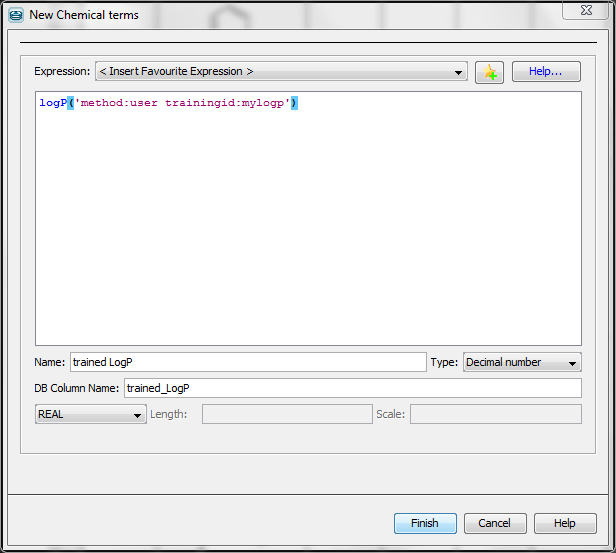
Fig. 3 Using Chemical Terms function for training in Instant JChem
Part of the results of this calculation is presented below. You can see the difference between the untrained (column LogP) and trained (column trained LogP) values.

Fig. 4 JChem table showing the untrained and trained logP values