This manual gives you a walk-through on how to use the Solubility Predictor:
Introduction
Aqueous solubility is one of the most important physico-chemical properties in modern drug discovery. It has impact on ADME-related properties like drug uptake, distribution and even oral bioavailability. Solubility can also be a relevant descriptor for property-based computational screening methods in the drug discovery process. Hence there is a significant interest in fast, reliable, structure-based methods for predicting aqueous solubility of promising drug candidates.
Predicting solubility of drug molecules is not a trivial computational task. The used model has to somehow calculate the intrinsic solubility for the compound, which is a crucial solubility parameter. ChemAxon's Solubility Predictor is able to calculate the intrinsic aqueous solubility. The prediction uses a fragment-based method that identifies different structural fragments in the molecule and calculates their solubility contribution. The implementation is based on the article of Hou et al.
The figure below shows a fragmented molecule using the fragmentation method behind the intrinsic solubility prediction.
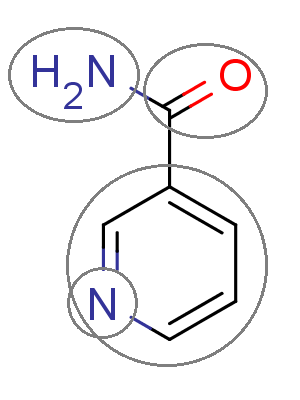
Fig. 1 The molecule is split into fragments to predict its solubility.
However, in many applications (such as therapeutic or lab measurements) it is also important to know the solubility in acidic/basic solutions, that is at a given pH. Therefore the model should also be able to calculate the pH--solubility profile of a compound. The original solubility predictor method has been extended so that it is able to calculate the pH--solubility profile.
The predictor can provide quantitative results, giving the solubility in logS, mg/mL or mol/L units. The predictive accuracy of the plugin is considered to be 1 logS unit. In case only an estimation about how well the compound is soluble, the plugin can give a solubility category as a qualitative measure.
The accuracy of the intrinsic solubility prediction was tested using two test sets in Hou et al. The two plots below show the experimental vs. predicted intrinsic solubility values and the deviation.

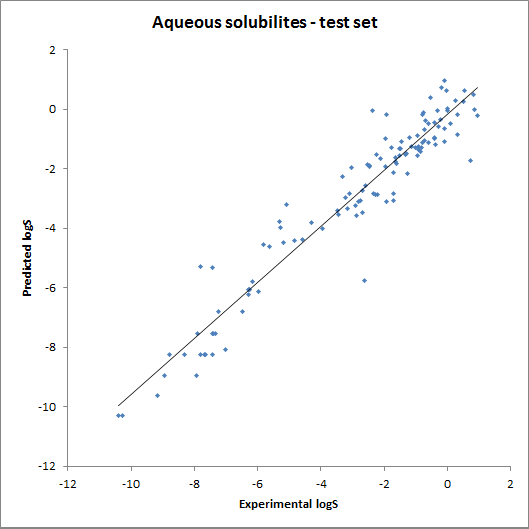
Fig. 2 Plots showing predicted vs. experimental intrinsic solubility values (for data see the reference)
Tests for pH--logS profile were also run. The two plots below show calculated and experimental pH-logS profiles for different acidic, basic and zwitter-ionic compounds.
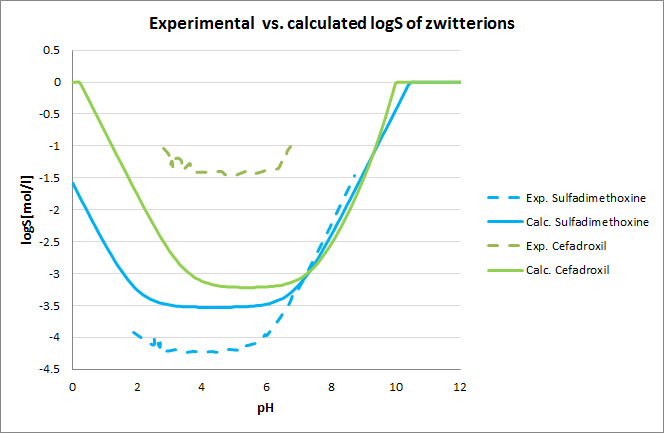

Fig. 3 Plots showing calculated vs. experimental pH-logS profiles for different compound sets (for data see the reference)
Usage
The Solubility Predictor is currently available in three ways.
MarvinSketch
The solubility predictor is integrated into Marvin Sketch as a plugin, which makes prediction fast and easy. The Solubility Plugin can be reached via the Calculations > Solubility menu.
Menu system
The menu system of the Solubility Plugin has File, Options and Help menus.
File menu
The File menu can be used to export the results into PDF, or to close the result window.
 Export to PDF: exports the results into a PDF file, which can be used as a report.
Export to PDF: exports the results into a PDF file, which can be used as a report.- Exit: closes the result window.
Options menu
The Options menu can be used to set the options of the solubility calculation.
- Measurement Unit: sets the solubility measurement unit. This can be logS (default), mol/l, or mg/ml.
- Restore default settings: restores the default settings of the calculation.
Help menu
The Help menu opens the help guide of the predictor.
Result window
The result window displays the pH-logS plot and a table with prediction results given in one of the following ways :
- Solubility information: displays intrinsic solubility value, solubility at pH 7.4 and a qualitative category for the predicted solubility. These categories are:
- low: if solubility is < 0.01 mg/ml
- moderate: if solubility is between 0.01 and 0.06 mg/ml
- high: if solubility is > 0.06 mg/ml
- pH-Solubility table: displays a table containing the predicted pH-solubility values.
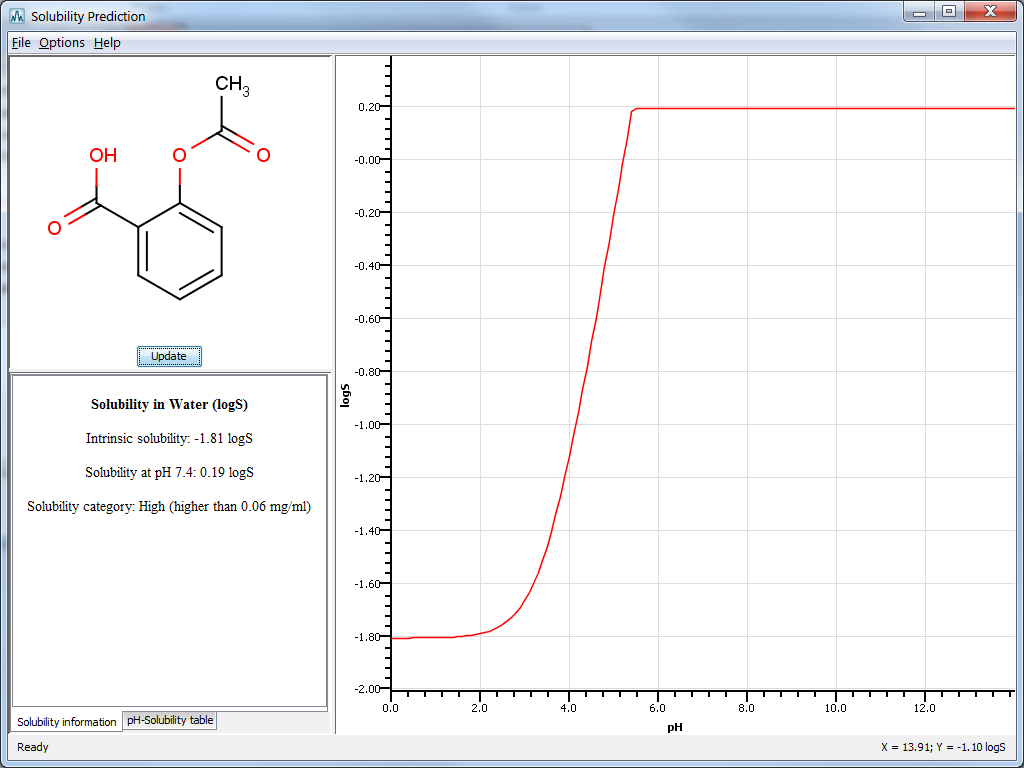
Fig. 4 The Solubility Plugin result window in MarvinSketch
cxcalc
The solubility predictor is integrated into the cxcalc command line tool. The command syntax is
cxcalc [general options] [input files/strings] logs [logs options] [input files/strings]
where the logS options are the following:
logs options:
-h --help this help message
-U --unit measurement unit [mg/ml | mol/l | logS] (default:
logS)
-i --intrinsic intrinsic solubility (default: false)
-c --category solubility category (default: false)
-H --pH solubility at this pH (default: not set)
-l --lower (default: 0)
-u --upper (default: 14)
-s --step (default: 1)
Some examples on how to use the solubility predictor via cxcalc:
Calculating intrinsic solubility and solubility at pH 7.4 for compounds:
cxcalc logs -i true -H 7.4 molecules.smiles
Calculating solubility values between pH 7.0 and 13.0 in mol/l unit:
cxcalc logs -U mol/l -l 7.0 -u 13.0 molecules.smiles
Predicting qualitative solubility category:
cxcalc logs -c true test.mol
Chemical Terms
The solubility predictor is also integrated into ChemAxon's Chemical Terms language. The solubility can be calculated by the logS() function that has two parameters:
- A unit parameter, which could be 'mg/ml', 'mol/l', 'logS', or 'category'. In case of 'category' is used, qualitative solubility is calculated. If no unit parameter is given, logS unit is used.
- A pH parameter, which is a real number (e.g. '7.4') and sets the pH for solublity calculation. If no pH parameter is given, intrinsic solubility is calculated.
The following examples show how the functions above can be used with the Chemical Terms evaluator command line tool:
Calculating intrinsic solubility for acetic acid in logS unit:
evaluate -e "logS()" "CC(O)=O"
Calculating solubility at pH 7.0 in mol/l unit:
evaluate -e "logS('7.0', 'mol/l')" molecule.molDetermines qualitative solubility category at pH 7.4:
evaluate -e "logS('7.4', 'category')" molecule.mol
References
Hou, T. J.; Xia, K.; Zhang, W.; Xu, X. J. ADME Evaluation in Drug Discovery. 4. Prediction of Aqueous Solubility Based on Atom Contribuition Approach. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2004, 44, 266-275