 |
|
|
|
|
|
-
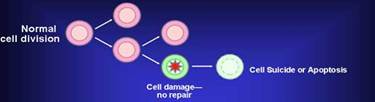
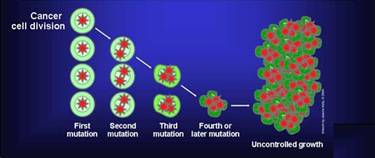
Cancer arises from loss of normal growth control.
-
In normal tissues, the rates of new cell growth and old cell death are kept in balance.
 |
 |
| Source: www.cancer.gov |
|
|
Invasion and Metastases |
-
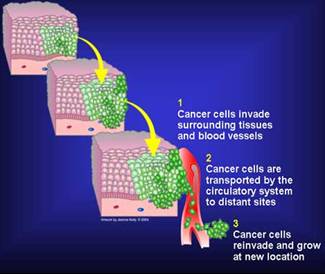
During the development of cancer, tumor invades nearby tissues by breaching the basement membrane.
-
Basement membrane is a sheet of proteins and other substances to which epithelial cells adhere and form a barrier between tissues.
-
Once tumor breaks this membrane, cancerous cells invade surrounding tissue and the blood stream via lymphatic vessels and discharge contents into the blood.
-
Tumor cells that invade lymphatic vessels become trapped in lymph nodes.
-
Cells that gain access to blood vessels are disseminated to various parts of the body, bones, lungs and brains
-
At distant sites, cancer cells form secondary tumors, or metastases.
-
Ability to metastasize makes cancer a lethal disease.
-
Primary tumor can be controlled by many available therapies.
-
It is the disseminated disease that proves fatal to the host eventually.
|
| Top |
Malignant and Benign Tumors |
-
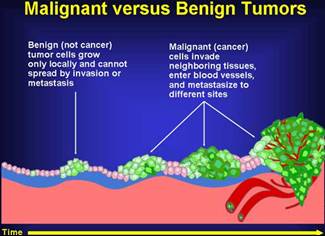
Tumors are classified as either being benign or malignant based on whether they can spread by invasion and metastases.
 |
| Source: www.cancer.gov |
-
Benign tumors cannot spread by invasion and metastases. They grow locally.
-
Malignant tumors are capable of spreading by invasion and metastases.
|
Microscopic Appearance of Cancer Cells |
| Top |
-
Normal
-
Cancerous
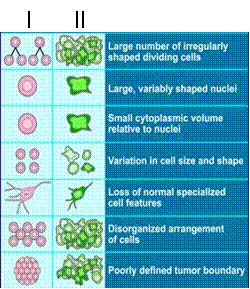 |
| Source: www.cancer.gov |
|
|
| Top |
 |
|
| Top |
-
Change in bowel or urine habits
-
A sore throat that does not heal
-
Unusual bleeding or discharge
-
Thickening of lump in breast or elsewhere
-
Indigestion or difficulty in swallowing
-
Obvious change in warts or moles
-
Nagging cough or hoarseness
|
|
| Cervical Cancer Screening |
PAP test |
| Breast cancer screening |
Mammogram |
| Prostrate and ovarian cancer screening |
PSA test |
| Colon cancer screening |
Fecal occult blood test |
|
|
-
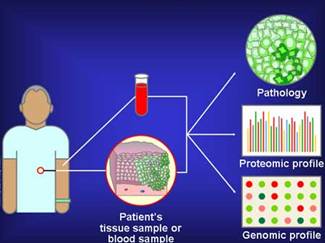
When preliminary symptoms, PAP test, mammogram, PSA test, FOBT/colonoscopy indicate possible existence of cancer, biopsy is performed.
-
Biopsy is surgical removal of a small piece of tissue for microscopic examination.
-
For leukemia, small blood sample serves the purpose.
 |
| Source: www.cancer.gov |
-
Microscopic examination reveals the presence of malignant/benign tumors.
-
Micro arrays determine the genes responsible.
-
Proteomic profiles analyze the protein activity.
|
|
| Top |
-
Microscopic examination reveals information regarding behavior of tumor and its response to treatment.
-
Cancer with more number of highly dividing cells tend to grow more quickly, spread faster to other organs and are less responsive to therapy when compared to cancers which have a normal appearance.
-
Based on these differences under a microscope, doctors assign a numerical grade to cancer. Low number grade (I & II) refers to cancers with fewer cell abnormalities than those with higher numbers (III & IV).
|
|
-
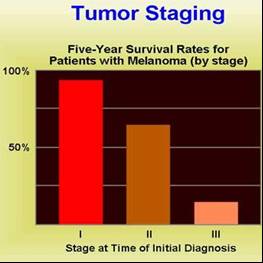
Tumor staging is done, once cancer has been diagnosed to determine how far the disease has progressed. Commonly asked questions are :
-
How large is the tumor and how deeply has it invaded the surrounding tissue.
-
Have cancer cells spread to regional lymph nodes?
-
Has cancer metastasized to other regions of the body?
 |
| Source: www.cancer.gov |
Based on the answers to these queries, cancer is assigned a stage. Patient’s chances for survival are better when cancer is detected at a lower stage.
|
|
| Top |
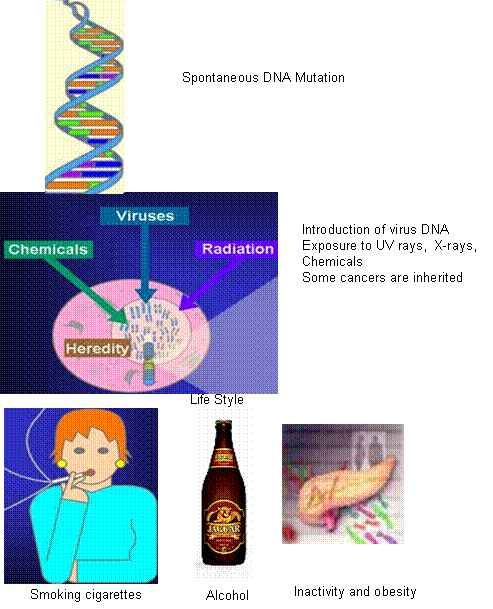
-
Chemicals, radiation, viruses and heredity all contribute to the development of cancer by triggering changes in cell’s genes.
-
Chemicals and radiation act by damaging genes.
-
Viruses introduce their own genes into cells.
-
Heredity passes on alterations in genes that make a person susceptible to cancer
-
Genes are a set of inherited instructions that lie within a person’s chromosome.
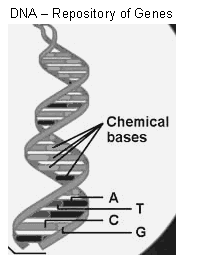 |
| Source: www.cancer.gov |
-
Genes are mutated in various ways as part of the mechanism by which cancer arises.
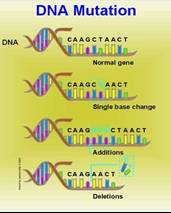 |
| Source: www.cancer.gov |
-
The simplest type of mutation involves a change in a single base along the base sequence.
-
Sometimes large segments of DNA molecule are accidentally repeated, deleted and moved.
|
Molecular basis of cancer |
| Top |
| |
|
| Top |
-
Avoid carcinogenic chemicals, carcinogenic radiation and cancer viruses or bacteria
-
Avoid tobacco
-
Protection against excessive exposure to sunlight
-
Limit alcohol and tobacco
-
Diet: limit fats and calories; consume fruits and vegetables
-
Avoid cancer viruses
-
Avoid carcinogens at work
|
The Cancer Genome Project
|
| Top |
-
All cancers occur due to abnormalities in DNA sequence.
-
Throughout life, the genome within cells of human body is exposed to mutagens and suffers mistakes in replication.
-
These corrosive influences result in progressive, subtle divergence of the DNA sequence in each cell from that originally constituted in the fertilized egg.
-
Occasionally, one of these somatic mutations alters the function of a critical gene, providing growth advantage to the cell in which it has occurred and resulting in the emergence of an expanded clone derived from the cell.
-
The identification of genes that are mutated and hence drive oncogenesis has been a central aim of cancer research since the advent of recombinant DNA technology.
-
Cancer genome project is using the human genome sequence, mutation and deletion techniques to identify somatically acquired sequence variants/mutations and hence identify genes critical in the development of human cancers.
| The most common causes of death from cancer worldwide 2002 estimates |
|
|
|
|

