AutoMapper
Introduction
AutoMapper is a tool that performs automated chemical reaction mapping. It assigns atom maps to
the atoms of a reaction, so that the same map number will identify the corresponding atoms on the
two sides of the reaction arrow (reactant side and product side). Atom mapping reflects the
mechanism of the reaction.
Features
AutoMapper provides the following features:
- Map reactions in various mapping styles;
- Complete: All atoms of a reaction will be mapped.
- Changing: Atoms connected to forming, breaking, or modified bonds, and orphan
atoms (they have no matching pair on the other side of the reaction arrow) will be mapped.
- Matching: Atoms present on both sides of the reaction will be mapped.
- Preserve the original maps of a partially mapped reaction;
- Mark reaction center. The following bonds will be marked:
 Make or break: bond is made or broken in the reaction;
Make or break: bond is made or broken in the reaction; Change:
type of the bond has changed during the reaction (e.g., single bond to double bond).
Change:
type of the bond has changed during the reaction (e.g., single bond to double bond).
Usage
Automapper is integrated into and used by the following ChemAxon products:
Algorithm
AutoMapper algorithm is based on Maximum Common Substructure (MCS) and Minimal Chemical Distance
(MCD) algorithms.
Examples
Example 1: Comparison of different mapping styles
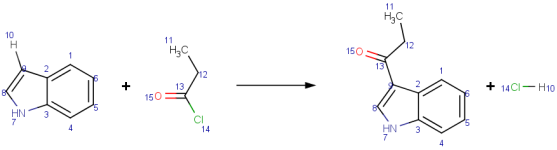 |
Fiedel-Crafts acylation of indole with propionyl chloride.
Mapping style: Complete
All atoms of the reaction are mapped. |
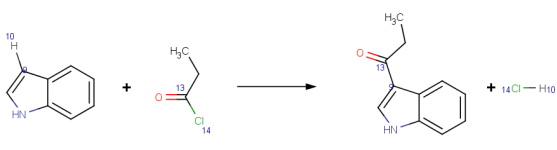 |
Fiedel-Crafts acylation of indole with propionyl chloride.
Mapping style: Changing
AutoMapper maps atoms connecting to forming and breaking bonds. |
 |
Fiedel-Crafts acylation of indole with propionyl chloride.
Mapping style: Matching
AutoMapper's Matching style maps atoms present on both sides of the reaction.
In a balanced chemical reaction, Matching style mapping does not differ from Complete style mapping.
|
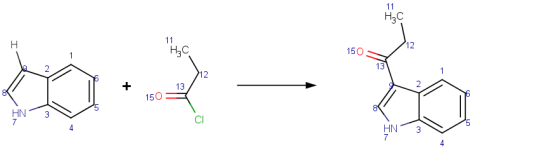 |
Fiedel-Crafts acylation of indole with propionyl chloride.
Mapping style: Matching
AutoMapper's Matching style maps atoms present on both sides of the reaction;
see
missing map numbers on explicit hydrogen and chlorine on the reactant side.
|
Example 2: Demonstration of reaction center bond marks and Changing mapping style
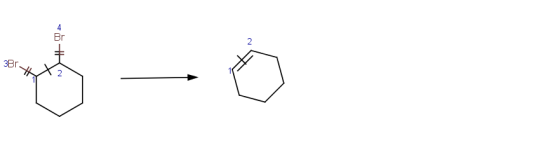 |
Dehalogenation of 1,2-dibromocyclohexane
Mapping style: Changing
Bonds between atoms 1 and 3, and between atoms 2 and 4 have broken in this reaction, while bond between
atoms 1 and 2 has changed from single to double bond. |
Links
 Make or break: bond is made or broken in the reaction;
Make or break: bond is made or broken in the reaction; Change:
type of the bond has changed during the reaction (e.g., single bond to double bond).
Change:
type of the bond has changed during the reaction (e.g., single bond to double bond). 


