This manual gives you a walk-through on how to use the Tautomer Generation Plugin:
Introduction
Tautomers are organic compounds that are interconvertible by tautomerization.Tautomerization results in the formal migration of a hydrogen atom or proton, accompanied by a switch of a single bond and an adjacent double bond. Usually the catalysts of these reactions are acids or bases. In solution there is an equilibrium state between the tautomeric forms. Some types of tautomers: ketone-enol, amid-imidic acid, lactam-lactim, enamine-imine tautomeric forms.
The Tautomer Generation Plugin is able to calculate tautomers based on many user-defined options.To have more information on tautomers and our tautomer generation method, see the tautomerization reference page.
Options
General options
The following general (calculation-related) options can be set in the Tautomers Options window:
-
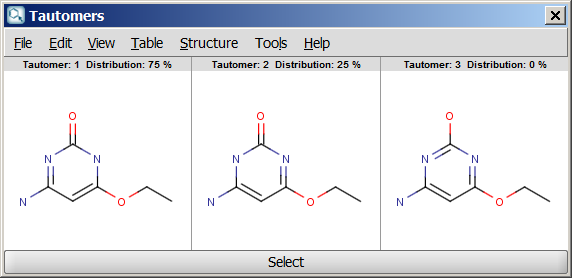
- Dominant tautomer distribution: displays the percentage of different tautomers present at the given pH.
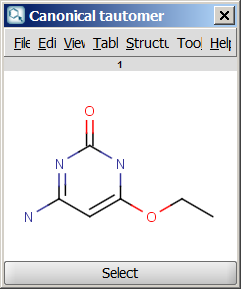
- Canonical tautomer: calculates only the canonical tautomer of the structure; rational tautomer generation mode can be activated.
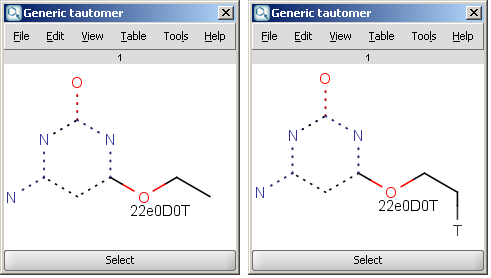
Generic tautomer: used for the identification of tautomers in JChem databases.
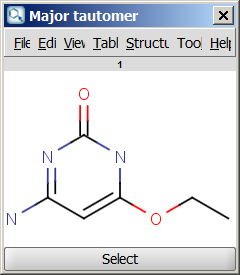
- Major tautomer: gives the first structure from the dominant tautomer distribution.
- All tautomers: combinatorially generates all possible tautomers. If any deuterium or tritium is involved in the tautomerization, isotopes are not removed; rational tautomer generation mode can be activated.
- Max. number of structures: maximize the number of structures to display. This number is the sum of unique tautomeric count and degenerated tautomeric count; however, only unique tautormers are displayed, their degenerated tautomeric pairs are not.
- Consider pH effect: takes into account the protonation states at given pH. Applicable for Major tautomer and Dominant tautomer distribution calculations.
- Rational tautomer generation: the tautomerization products are generated according to empirical rules. Rational tautomer generation narrows down the possible tautomerization paths and leads to chemically more feasible products.
To have more information on rational tautomer generation, see the tautomerization reference page. - Single fragment mode: if checked (default), the results are displayed in separate windows; if unchecked, the calculation handles unlinked molecules together and results appear in the same window.
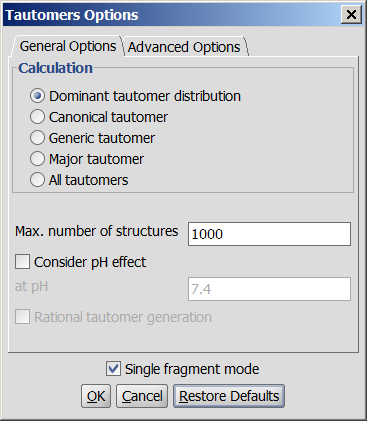
Fig. 1 General Options panel in the Tautomers Options window
Advanced options
The following advanced (calculation- and display-related) options can be set in the Tautomers Options window:
- Decimal places: setting the number of decimal places used for displaying the tautomer distribution values.
- Set max. allowed length of the tautomerization path: sets the number of bonds (a path) which are considered by displacing a double bond.
- Protect aromaticity: if checked (default), the aromaticity is kept.
- Protect charge: if checked (default), charges of atoms are kept during calculation.
- Exclude antiaromatic compounds: if checked (default), any tautomer structure having an antiaromatic ring system will be discarded.
- Protect double bond stereo: if checked, all double bonds with stereo information remain intact. If unchecked (default), tautomer regions will lose the double bond stereo information, any other stereo information in the molecule is kept intact.
- Protect all tetrahedral stereo centers: if checked, stereocenters are not included in the tautomerization. If unchecked (default), tautomer regions will lose the tetrahedral stereo information, any other stereo information in the molecule is kept intact.
- Protect labeled tetrahedral stereo centers only: if checked, stereocenters labeled with chiral flag or MDL Enhanced Stereo Representation flags will not be included in tautomerization, other stereocenters will.
- Single fragment mode: if checked (default), the results are displayed in separate windows, if unchecked, the calculation handles unlinked molecules together and results are in the same window.
- Protect ester groups: if checked, ester groups are not taking part in tautomerization.
- Ring-chain tautomerization is allowed: this option can be activated when "All tautomers" function is selected; if checked, tautomer generation will take into account the possibility of ring closure.
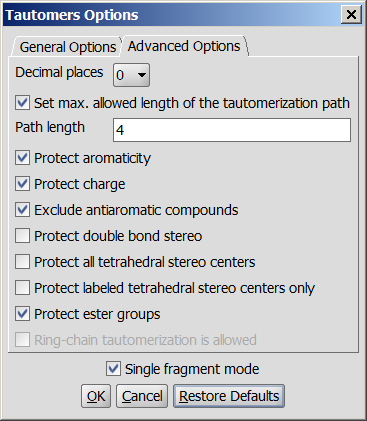
Fig. 2 Advanced Options panel in the Tautomers Option window
Examples
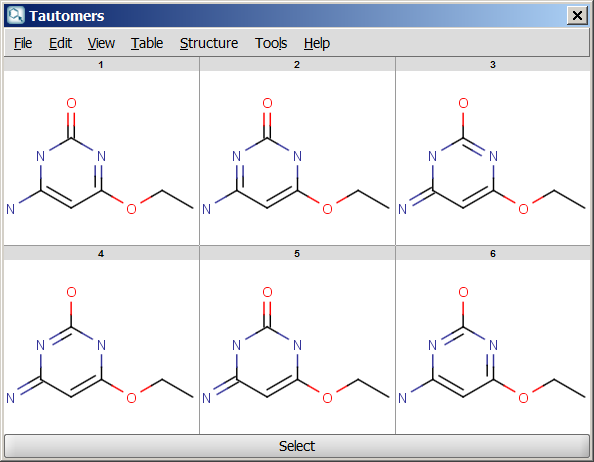
An an example we calculated the different tautomers for 4-amino-6-ethoxypyrimidin-2-ol:
References
- Smith, M. B.; March, J. Advanced Organic Chemistry, 5th ed., Wiley Interscience, New York, 2001; pp 1218-1223. ISBN 0471585890