Valence Calculations
Introduction
The Valence Calculator has 3 functionality:
- calculate if there is valence error.
- set the appropriate amount of implicit hydrogen
The functionality of the Valence Calculator is focused mainly on
the organic compounds, although the inorganic compounds not
containing transition-metal atoms are also supported.
Molecules
1st Group
Hydrogen
- Default: H+
- Molecules:
- Neutral atoms:1 bond is accepted
- Charged atoms: Not allowed in molecules.
- Radical: Not allowed in molecules.
- Ions: H+, H-
- Radical:
- H· is accepted
- H without radical and charge or bond is not accepted.
Lithium (Li), Sodium (Na), Potassium (K), Rubidium (Rb), Caesium (Cs),
Francium (Fr)
- Default: Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr respectively.
- Molecules:
- Neutral atoms:1 bond is accepted.
- Charged atoms: Not allowed in molecules.
- Radical: Not allowed in molecules.
- Ions:
Li+, Na+, K+,
Rb+, Cs+, Fr+ are accepted.
- Radical: Me· is accepted
2nd Group
- Default: Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra respectively.
- Molecules:
- Neutral atoms: 2 bonds are accepted.
- Charged atoms:
Each added charge decreases by one the number of possible
bonds.
- Radical: Each added radical decreases by one
the number of possible bonds
- Ions:
- Be2+, Mg2+, Ca2+,
Sr2+, Ba2+
Ra2+ are accepted
- Radicals: ·Me+ is accepted
13th Group
Boron
- Default: BH3
- Molecules:
- Neutral atoms:
- Implicit Hydrogens are added to have 3 bonds.
- 4 bonds are accepted with 1 negative charge on the boron
atom.
- 5 or more bonds are forbidden.
- Charged atoms:
- Positive charge:
Every added charge
decreases by one the number of possible bonds.
Maximum charge accepted is +3.
- Negative charge:
BH4-,
BH32-
BH23-
BH4- and B5- are accepted.
- Radicals:
Every added radical on these atoms
decreases by one the number of necessary bonds.
- Aromatic compounds:
Boron may form aromatic bonds as well.
Aluminium (Al), Gallium (Ga), Indium (In), Thallium (Th)
- Default: Al, Ga, In, Th respectively.
- Molecules:
- Neutral Atoms: 3 bonds around these atoms are accepted.
- Charged atoms:
- Positive charge:
Every added charge
decreases by one the number of possible bonds.
Maximum charge accepted is +3.
- Negative charge:
4- charge with 4 ligands is accepted.
- Radicals:
Every added radical on these atoms
decreases by one the number of necessary bonds.
- Ions:
- Al+, Ga+, In+, Rb+,
Al3+, Ga3+, In3+,
Rb3+
are accepted.
- Radical: ·Me2+ and
·̣Me·
are allowed.
14th Group
Carbon (C), Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge)
- Default:
CH4,
SiH4,
GeH4 respectively.
- Molecules:
- Neutral atoms
Implicit Hydrogens are added to have 4 bonds.
5 or more bonds are forbidden.
- Charged atoms:
Every added charge on these atoms
(no matter it is positive or negative)
decreases by one the number of possible bonds.
Maximum charge accepted is ±4.
- Radical:
Every added radical on these atoms
decreases by one the number accepted of bonds.
- Aromatic compounds:
Carbon may form aromatic bonds as well.
Tin (Sn)
- Default: Sn
- Molecules:
- Neutral atoms:
Implicit Hydrogens are added to have 4 bonds
(if Tin has at least 1 bond).
5 or 6 bonds are also accepted.
- Charged atoms:
- Positive charge:
Every added charge (no matter it is positive or negative)
decreases by one the number of possible bonds.
Maximum charge accepted is +4.
- Negative charge: Not allowed.
- Radical:
Every added radical on these atoms
decreases by one the number accepted of bonds.
- Ions:
- Sn2+ and Sn4+ are accepted.
- Other:
- Sn with 2 electrons in bonds and with at least to coordinate bonds are accepted.
Lead (Pb)
- Default: Pb
- Molecules:
- Neutral atom:
- 1 or 2 bonds: 1 or 0 implicit hydrogen is added,
respectively.
- 3 or 4 bonds: 1 or 0 implicit hydrogen is added,
respectively.
- 5 or 6 bonds are accepted.
- More than 6 bonds are forbidden.
- Charged atom:
- Positive charge:
Every added charge (no matter it is positive or negative)
decreases by one the number of possible bonds.
Maximum charge accepted is +4.
- Negative charge: Not allowed.
- Radical:
Every added radical on these atoms
decreases by one the number accepted of bonds.
- Ions:
- Pb2+ and Pb4+ are accepted.
15th Group
Nitrogen (N)
- Default: NH3
- Molecules:
- Neutral atoms
- Implicit hydrogens are added to have 3 bonds
(if nitrogen has at least 1 bond).
- More than 3 bonds are forbidden.
- If nitrogen has 4 ligands, charge is not set, hence
not accepted
- Pentavalent N is accepted in traditional form by default,
but keep in mind that these forms are not
correct. Use the "ylide" from of the N atom
which satisfies the correct valence electron count:
| traditional form |
"ylide" form |
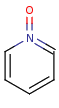 |
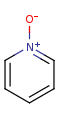 |
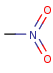 |
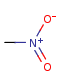 |
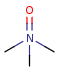 |
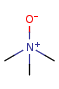 |
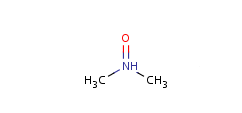 |
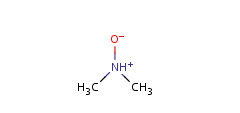 |
- It's possible to accept only the "ylide" form using the MoleculeGraph.setValenceCheckOptions() function.
- Charged atoms in a molecule:
- Positive charge:
- 1+: 4 bonds needed (incluing implicit hydrogens)
- 2+: 3 bonds needed (incluing implicit hydrogens)
- 3+: 2 bonds needed (incluing implicit hydrogens)
- 4+: 1 bonds needed (incluing implicit hydrogens)
- 5+: 0 bonds needed (incluing implicit hydrogens)
- 6+ or more: not allowed
- Negative charge: Every added negative charge
decreases by one the number of possible bonds.
Maximum charge accepted is -3.
- Radical:
Every added radical on these atoms
decreases by one the number of bonds.
Maximum three added radical is allowed.
- Aromatic compounds:
Nitrogen may form aromatic bonds
as well.
Phosphorus (P), Arsenic (As), Antimony (Sb), Bismuth (Bi)
- Default: PH3, AsH3,
SbH3, Bi
- Molecules:
- Neutral atoms:
- 1 bond: 2 implicit Hydrogens are added.
- 2 bond: 1 implicit Hydrogen is added.
- 3 bond: 0 implicit Hydrogen is added.
- 4 bond: 1 implicit Hydrogen is added.
- 5 bond: 0 implicit Hydrogen is added.
- More than 5 bonds are forbidden
- Charged atoms in a molecule:
- Positive charge:
- 1+: 4 bonds are necessary (including implicit Hydrogens).
- 2+: 3 bond is necessary (including implicit Hydrogens).
- 3+: 2 bond is allowed.
- 4+: 1 bond is necessary (including implicit Hydrogens).
- 5+: 0 bond is allowed.
- 6+ or more: not allowed
- Negative charge: Every added negative charge
decreases by one the number of possible bonds.
Maximum charge accepted is -3.
- Radical:
Every added radical on these atoms
decreases by one the number of bonds.
Maximum three added radicals are allowed.
- Aromatic compounds:
Phosphorus may form aromatic bonds
as well.
16th Group
Oxygen (O)
- Default: H2O
- Molecules:
- Neutral atom:
- Implicit Hydrogens are added to have 2 bonds
(if Oxygen has at least 1 bond).
- More than 2 bonds are forbidden
- Charged atom:
- Positive charge:
- 1+: 3 bonds are necessary
(including implicit Hydrogens).
- 2+: 4 bonds are necessary
(including implicit Hydrogens).
- 3+: 3 bonds are necessary
(including implicit Hydrogens).
- 4+: 2 bonds are necessary
(including implicit Hydrogens).
- 5+: 1 bonds are necessary
(including implicit Hydrogens).
- 6+: 0 bonds are necessary
(including implicit Hydrogens).
- Negative charge:
One or two the negative charges are accepted,
with one or zero ligands, respectively.
- Radical:
Every added radical on these atoms
decreases by one the number of bonds.
Maximum two added radical is allowed.
- Aromatic compounds:
Oxygen may form aromatic bonds
as well.
Sulfur (S), Selenium (Se), Tellurium (Te), Polonium (Po)
- Default: H2S, H2Se,
H2Te, H2Po
- Molecules:
- Neutral atom:
- 1 bond: 1 implicit Hydrogen is added
- 2 bond: 0 implicit Hydrogen is added
- 3 bond: valence error on S/Se/Te/Po atom
- 4 bond: 0 implicit Hydrogen is added
- 5 bond: 1 implicit Hydrogen is added
- 6 bond: 0 implicit Hydrogen is added
- More than 6 bonds are forbidden
- Charged atom:
- Positive charge:
- Sulfur (S):
- 1+: 3 or 5 bonds are necessary
(including implicit Hydrogens).
- 2+: 4 bonds are necessary
(including implicit Hydrogens).
- 3+: 3 bonds are necessary
(including implicit Hydrogens).
- 4+: 2 bonds are necessary
(including implicit Hydrogens).
- 5+: 1 bond is necessary
(including implicit Hydrogens).
- 6+: 0 bond is allowed.
- 7+ or more: not allowed.
- Selenium (Se), Tellurium (Te), Polonium (Po):
- 1+: 1, 3 or 5 bonds are necessary
(including implicit Hydrogens).
- 2+: 0 or 4 bonds are necessary
(including implicit Hydrogens).
- 3+: 1 or 3 bonds are necessary
(including implicit Hydrogens).
- 4+: 0 or 2 bonds are necessary
(including implicit Hydrogens).
- 5+: 1 bond is necessary
(including implicit Hydrogens).
- 6+: 0 bond is allowed.
- 7+ or more: not allowed.
- Negative charge:
- 1-: 1 bond accepted.
(Exception: 2 double bonded oxygens and
1 more ligand connected by a single bond)
- 2-: Zero ligand is accepted
- Radical: Every added radical on these atoms
decreases by one the number of bonds.
Maximum 2 added radical is allowed.
- Aromatic compounds:
Sulfur may form aromatic bonds
as well.
17th Group
- Default:HF, HCl, HBr, HI, HAt
- Molecules:
- Neutral atoms: 1 bond is allowed.
Exceptions:
- 3 valence:
- Two of the ligands should be F, Cl or oxygen;
and one more atom from the 14th, 15th,
16th columns.
- Double bonded oxygen and one any other atom from
14th, 15th, 16th columns are also accepted.
- 5 valence:
- Four of the ligands should be F, Cl or oxygen;
and one more atom from the 14th, 15th,
16th columns. Double bonded oxygens are accepted.
- 7 valence:
- Halogen oxoacids:
- HXOy, where X = Cl, Br, I or At; and
y = 2, 3 or 4.
- Charged atom:
- 1+: 2 bonds are necessary.
- Ions:
- F-, Cl-, Br-,
I-, At- are accepted.
- Radicals:
- 1 Radical with 0 bond around the halogen atom is accepted.
18th Group
- Default:He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rd
- Molecules: 0 bond is accepted.
- Exceptions:
The following xenon compounds are accepted:
XeF2, XeF4, XeF6,
XeO3, XeO4
XeOF4, XeO2F2,
XeO3F2.
- Ions: 0 charge is accepted
- Radicals: 0 radical is accepted
Valence calculator provides two ways to check the valence of an atom
having aromatic bonds:
- Local Aromatic Valence Calculator uses only
the bond and ligand information of the considered atom
to do valence calculations. Hence, this method is faster, but often
chemically incorrect.
- Global Aromatic Valence Calculator examine the
whole aromatic ring system to calculate the valence of one of
its atoms. This method is, therefore, slower but chemically more
reliable. We recommend the usage of this method, when the not the
speed but the chemical reliablity of the valence calculations are
important.
Local Aromatic Valence Calculator
Aromatic atoms are sorted into four groups, i.e. boron-like,
carbon-like, nitrogen-like and oxygen-like atoms according to their
behavior.
Boron-like atoms
- Boron-like atoms: B, C+
- Valence can not be calculated exactly.
- One aromatic bond:
- Accepted with two implicit hydrogens.
- Accepted with one single bond.
- Accepted with one single bond and one other single bond
or one radical or one
implicit hydrogen or one attachment point.
- Accepted with one double bond.
- Two aromatic bonds:
- Accepted with no other bond, one single bond,
one implicit hydrogen or
one radical or one attachment point.
- Three aromatic bonds:
- Accepted with no other bonds, implicit hydrogens,
radical or attachment point.
Carbon-like atoms
- Carbon-like atoms: B-, C, N+,
P+
- Valence can be calculated exactly.
- One aromatic bond:
- Accepted with two implicit hydrogens.
- Accepted with one single bond.
- Accepted with one single bond and one other single bond
or one double bond or one radical or one
implicit hydrogen or one attachment point.
- Accepted with one double bond.
- Accepted with one double bond and
one radical or one
implicit hydrogen or one attachment point.
- Two aromatic bonds:
- Accepted with no other bond, one single bond,
one implicit hydrogen or
one radical or one attachment point.
- Three aromatic bonds:
- Accepted with no other bond, implicit hydrogen,
radical or attachment point.
Nitrogen-like atoms
- Nitrogen-like atoms: C-, N , P,
O+, S+
- Valence can not be calculated exactly.
- One aromatic bond:
- Accepted with two implicit hydrogens.
- Accepted with one single bond.
- Accepted with one single bond and one other single bond
or one radical or one
implicit hydrogen or one attachment point.
- Accepted with one double bond.
- Two aromatic bonds:
- Accepted with no other bond, one single bond,
one implicit hydrogen or
one radical or one attachment point.
- Three aromatic bonds:
- Accepted with no other bond, implicit hydrogen,
radical or attachment point.
Oxygen-like atoms
- Oxygen-like atoms: N-, P-,
O, S
- Valence can be calculated exactly.
- One aromatic bond:
- Accepted with zero implicit hydrogens.
- Accepted with one single bond.
- Two aromatic bonds:
- Accepted with no other bond, implicit hydrogen,
radical or attachment point.
- Three aromatic bonds:
Exocyclic double bonds
When an atom two aromatic bonds, it may have a double bond with
specific ligand:
- Carbon: C, N, P, O, S atoms are possible ligand atoms.
- Nitrogen, Phosphorous, Sulfur: Only O is possible ligand atom.
- Nitrogen and Phosphorous with 1+ charge: Any atom can be
ligand.
Global Aromatic Valence Calculator
Global Aromatic Valence Calculator is not yet implemented.
Superatom S-Groups
S-group attachment points are considered as bonds. Three cases are possible:
- There is one S-group attachment point around the
investigated atom, that abbreviates one single bond;
- There are two S-group attachment points around the
investigated atom, both of them abbreviate one single bond;
- There is one S-group attachment point around the
investigated atom, that abbreviates one double bond.
When there is a valence error in an S-group, it is indicated in its
expanded and contracted state as well.
Query Properties
If valence property is set, then the Valence Calculator uses that value,
v,
as the number of bond order.
- Default: AHv
- Molecules:
- Neutral atoms: Maximum v bonds are accepted.
- Ions and Radicals: According to the definition of the
valence property, charge and radical is not taken into account
when the valence is calculated.
Other query properties are not handled by the valence calculator.
Special atoms
Special atoms are not handled by the valence calculator.







